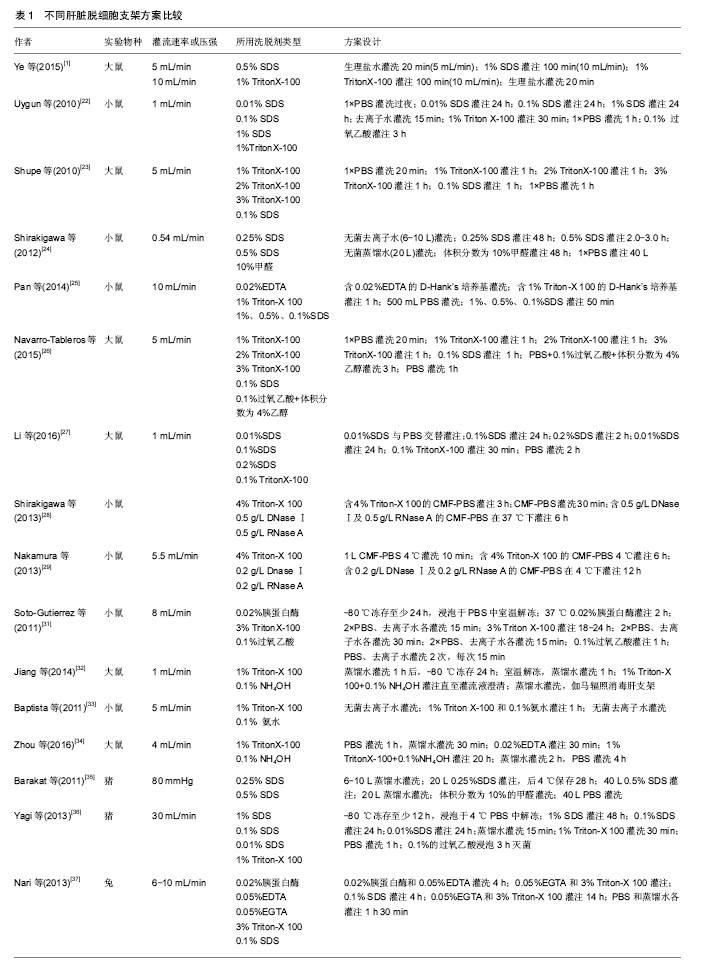
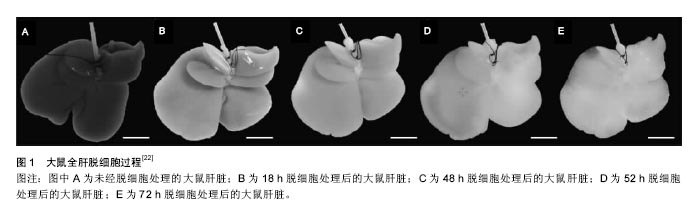
| [1]Ye JS, Stoltz JF, de Isla N, et al. An approach to preparing decellularized whole liver organ scaffold in rat. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl):159-166.[2]Fuhrman C, Jougla E, Nicolau J, et al. Deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in France, 1979-2002: a multiple cause analysis. Thorax. 2006;61(11):930-934.[3]Strong RW. Liver transplantation: current status and future prospects. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 2001;46(1):1-8.[4]Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut. 2009;58(12): 1690-1702.[5]Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartificial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001;34(3):447-455.[6]Struecker B, Raschzok N, Sauer IM. Liver support strategies: cutting-edge technologies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11(3):166-176.[7]Bañares R, Catalina MV, Vaquero J. Liver support systems: will they ever reach prime time. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2013;15(3):312.[8]Badylak SF. The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials. 2007;28(25):3587-3593.[9]Crapo PM, Gilbert TW, Badylak SF. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(12):3233-3243.[10]Faulk DM, Carruthers CA, Warner HJ, et al. The effect of detergents on the basement membrane complex of a biologic scaffold material. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):183-193.[11]Badylak SF, Taylor D, Uygun K. Whole-organ tissue engineering: decellularization and recellularization of three-dimensional matrix scaffolds. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2011;13:27-53.[12]Gattazzo F, Urciuolo A, Bonaldo P. Extracellular matrix: a dynamic microenvironment for stem cell niche. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(8):2506-2519.[13]Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. 2012; 196(4):395-406.[14]Watt FM, Huck WT. Role of the extracellular matrix in regulating stem cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8): 467-473.[15]Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326(5957):1216-1219.[16]Lee SY, Kim HJ, Choi D. Cell sources, liver support systems and liver tissue engineering: alternatives to liver transplantation. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(1):36-47.[17]Susick R, Moss N, Kubota H, et al. Hepatic progenitors and strategies for liver cell therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001; 944:398-419.[18]Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673-687.[19]史嘉玮,董念国,孙宗全,等.RGD肽固定对组织工程心脏瓣膜构建的作用[J].临床急诊杂志,2006,7(3):100-103.[20]Mattei G, Di Patria V, Tirella A, et al. Mechanostructure and composition of highly reproducible decellularized liver matrices. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2):875-882.[21]邬迪,王志伟.脱细胞技术及其在肝脏组织工程中的应用[J].江苏医药,2014,40(18):2176-2179.[22]Uygun BE, Soto-Gutierrez A, Yagi H, et al. Organ reengineering through development of a transplantable recellularized liver graft using decellularized liver matrix. Nat Med. 2010;16(7):814-820.[23]Shupe T, Williams M, Brown A, et al. Method for the decellularization of intact rat liver. Organogenesis. 2010;6(2): 134-136. [24]Shirakigawa N, Ijima H, Takei T. Decellularized liver as a practical scaffold with a vascular network template for liver tissue engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;114(5):546-551.[25]Pan MX, Hu PY, Cheng Y, et al. An efficient method for decellularization of the rat liver. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014;113(10):680-687.[26]Navarro-Tableros V, Herrera Sanchez MB, Figliolini F, et al. Recellularization of rat liver scaffolds by human liver stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(11-12):1929-1939.[27]Li Q, Uygun BE, Geerts S, et al. Proteomic analysis of naturally-sourced biological scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2016;75: 37-46.[28]Shirakigawa N, Takei T, Ijima H. Base structure consisting of an endothelialized vascular-tree network and hepatocytes for whole liver engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;116(6):740-745.[29]Nakamura S, Ijima H. Solubilized matrix derived from decellularized liver as a growth factor-immobilizable scaffold for hepatocyte culture. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013; 116(6): 746-753.[30]Keane TJ, Swinehart IT, Badylak SF. Methods of tissue decellularization used for preparation of biologic scaffolds and in vivo relevance. Methods. 2015;84:25-34.[31]Soto-Gutierrez A, Zhang L, Medberry C, et al. A whole-organ regenerative medicine approach for liver replacement. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(6):677-686.[32]Jiang WC, Cheng YH, Yen MH, et al. Cryo-chemical decellularization of the whole liver for mesenchymal stem cells-based functional hepatic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3607-3617.[33]Baptista PM, Siddiqui MM, Lozier G, et al. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology. 2011;53(2):604-617.[34]Zhou P, Huang Y, Guo Y, et al. Decellularization and Recellularization of Rat Livers With Hepatocytes and Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Artif Organs. 2016;40(3):E25-38.[35]Lee JS, Shin J, Park HM, et al. Liver extracellular matrix providing dual functions of two-dimensional substrate coating and three-dimensional injectable hydrogel platform for liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1): 206-218.[36]Yagi H, Parekkadan B, Suganuma K, et al. Long-term superior performance of a stem cell/hepatocyte device for the treatment of acute liver failure. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(11):3377-3388.[37]Miranda JP, Leite SB, Muller-Vieira U, et al. Towards an extended functional hepatocyte in vitro culture. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(2):157-167.[38]March S, Hui EE, Underhill GH, et al. Microenvironmental regulation of the sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype in vitro. Hepatology. 2009;50(3):920-928.[39]何宏亮,李建国,高志良.人工肝和干细胞在肝衰竭治疗中的进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2013,29(9):670-673.[40]Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, et al. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 2010;51(1):297-305.[41]Espejel S, Roll GR, McLaughlin KJ, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes have the functional and proliferative capabilities needed for liver regeneration in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(9):3120-3126.[42]Behbahan IS, Duan Y, Lam A, et al. New approaches in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells toward hepatocytes. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(3):748-759.[43]Lu TY, Lin B, Kim J, et al. Repopulation of decellularized mouse heart with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitor cells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2307.[44]Ebben JD, Zorniak M, Clark PA, et al. Introduction to induced pluripotent stem cells: advancing the potential for personalized medicine. World Neurosurg. 2011;76(3-4): 270-275.[45]Liu H, You S, Rong Y, et al. Newly established human liver cell line: a potential cell source for the bioartificial liver in the future. Hum Cell. 2013;26(4):155-161.[46]Zhang L, Zhao YH, Guan Z, et al. Application potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly in liver tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl): 137-143.[47]Allameh A. Recent technological advances in hepatogenic differentiation of stem cells relevant to treatment of liver diseases. Int J Pediatr. 2014;2(2):20.[48]Zhou Q, Li L, Li J. Stem cells with decellularized liver scaffolds in liver regeneration and their potential clinical applications. Liver Int. 2015;35(3):687-694.[49]Bao J, Shi Y, Sun H, et al. Construction of a portal implantable functional tissue-engineered liver using perfusion-decellularized matrix and hepatocytes in rats. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(5):753-766.[50]Zhou P, Lessa N, Estrada DC, et al. Decellularized liver matrix as a carrier for the transplantation of human fetal and primary hepatocytes in mice. Liver Transpl. 2011;17(4):418-427.[51]Caralt M, Velasco E, Lanas A, et al. Liver bioengineering: from the stage of liver decellularized matrix to the multiple cellular actors and bioreactor special effects. Organogenesis. 2014;10(2):250-259.[52]Lang R, Stern MM, Smith L, et al. Three-dimensional culture of hepatocytes on porcine liver tissue-derived extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2011;32(29):7042-7052.[53]Wang Y, Cui CB, Yamauchi M, et al. Lineage restriction of human hepatic stem cells to mature fates is made efficient by tissue-specific biomatrix scaffolds. Hepatology. 2011;53(1): 293-305.[54]Butter A, Aliyev K, Hillebrandt KH, et al. Evolution of graft morphology and function after recellularization of decellularized rat livers. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Dec 13. doi: 10.1002/term.2383. [Epub ahead of print][55]Park KM, Hussein KH, Hong SH, et al. Decellularized Liver Extracellular Matrix as Promising Tools for Transplantable Bioengineered Liver Promotes Hepatic Lineage Commitments of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(5-6):449-460.[56]Jiang WC, Cheng YH, Yen MH, et al. Cryo-chemical decellularization of the whole liver for mesenchymal stem cells-based functional hepatic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3607-3617.[57]Barakat O, Abbasi S, Rodriguez G, et al. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):e11-25.[58]Yagi H, Fukumitsu K, Fukuda K, et al. Human-scale whole-organ bioengineering for liver transplantation: a regenerative medicine approach. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(2): 231-242.[59]Barakat O, Abbasi S, Rodriguez G, et al. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):e11-25.[60]Nari GA, Cid M, Comín R, et al. Preparation of a three-dimensional extracellular matrix by decellularization of rabbit livers. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2013;105(3):138-143.[61]Damania A, Jain E, Kumar A. Advancements in in vitro hepatic models: application for drug screening and therapeutics. Hepatol Int. 2014;8(1):23-38.[62]Guzzardi MA, Domenici C, Ahluwalia A. Metabolic control through hepatocyte and adipose tissue cross-talk in a multicompartmental modular bioreactor. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(11-12):1635-1642.[63]Schmelzer E, Triolo F, Turner ME, et al. Three-dimensional perfusion bioreactor culture supports differentiation of human fetal liver cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):2007-2016.[64]Mazza G, Rombouts K, Rennie Hall A, et al. Decellularized human liver as a natural 3D-scaffold for liver bioengineering and transplantation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13079. |
.jpg)
.jpg)